

GONORRHEA & CHLAMYDIA (the 'clap' & 'Klamydia')
Summary
- Caused by bacteria germs; the infection starts 3 days to 3 weeks after having sex with an infected person.
- In men it causes a liquid (pus) to come out of the opening in the penis.
- Women usually don't have symptoms, but if untreated it can progress into a more serious disease and cause her not to be able to have babies in the future.
- These diseases can be completely cured by antibiotics if treated early.
| Gonorrhea Images | ||
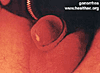 |
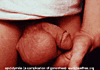 |
|
REMEMBER TO USE A CONDOM
Gonorrhea is discussed first because it is one of the most common STDs with an estimated two to three million cases a year in the United States. It's been with us since ancient times with biblical references although there were more citations of syphilis in published history. A Greek physician in Rome in the year130 AD coined the term from Greek (gonos=seed, rhea=flow) believing it was an involuntary flow of semen. There was very little reference to women having this disease until the 1900's.Chlamydia (pronounced "Klamydia") is discussed along with gonorrhea because the symptoms that it causes are very similar to gonorrhea. In general, it tends to be a bit more milder of a disease but this is not always so and it can cause many complications too. Like gonorrhea, chlamydia is also very common with over a million new cases each year in the United States.
These germs can be found in the genitals, throat, and the anal canal of an infected person. They can also affect the eyes but this is uncommon.
The groups most likely to get gonorrhea and chlamydia are young adults from ages 15 to 29. There are more cases of gonorrhea and chlamydia in the 15 to 19 year old age group when you consider that 15 to 19 year olds are less sexually active than 20 to 29 year olds.
The risk of spreading these diseases from a woman to a man following a single act of vaginal intercourse is said to be about 20 percent and it is likely that the rate of spread from men to women is even higher for each single act of sex. A big problem is that ten to fifteen percent of men and about seventy five percent of women do not have any symptoms. Most men and women who have symptoms will stop having sex and seek treatment. It is these individuals without symptoms who are spreading the disease more without even knowing it.
What causes gonorrhea and chlamydia?
Gonorrhea is caused by a bacteria that has an incubation period of from three to seven days but it may be as long as three weeks. The incubation period is the time from when the germ enters the body until it causes symptoms. Chlamydia is caused by a different bacteria germ whose incubation period is two to four weeks. It is possible to have the both germs at the same time.What are the symptoms of gonorrhea and chlamydia?
When a person has gonorrhea, he or she will try to get rid of it by producing white blood cells that fight infections. The combination of the gonorrhea germs and the white blood cells are called pus. It is usually white but may be clear and at times it may be gray or greenish. Sometimes blood is present in the pus. It is this liquid pus that is the way it is spread. In men, the pus is in the urethra which is the tube in the penis. Most men with gonorrhea will have this pus coming out of the penis as a discharge. Since the urethra is where urine comes out, men will often have a burning feeling when they urinate("pee") and they may feel like they have to urinate often. When a man has an infection in the urethra, we call it a urethritis (itis=inflammation). These symptoms are usually dramatic enough that the men will go to a health provider for treatment but in about ten to fifteen percent of the time, a man with gonorrhea will have little or no symptoms. In these cases, the man could spread the disease to others without knowing he is doing so.In men infected with chlamydia, the symptoms are nearly identical but they are usually milder. The pus is usually clearer than in gonorrhea and it is usually less in quantity. Also with chlamydia, the pain while urinating is usually much less than with a gonorrhea infection. We call the infection of the urethra with chlamydia non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU) or non-specific urethritis (NSU). To further complicate matters, there are other germs that can cause NGU but this online book will not get into them. They are usually treated with the same medicines that work on chlamydia. Again, as with gonorrhea, ten to fifteen percent of men will not have any symptoms and they can spread the disease without knowing it.
In women the gonorrhea and chlamydia germs do not usually live in the urethra but instead they live in the cervix. Since the cervix is way up in the vagina, women usually do not have many symptoms and when they do have symptoms, they are usually mild. Women do not feel pain on the cervix and even if pus is produced there, it usually is not much and it is hard to tell the difference from the woman's normal vaginal discharge. So, in about 85-90 percent of the time when a woman has gonorrhea or chlamydia, she has no symptoms. In the other ten or fifteen percent, the symptoms are pain urinating, vaginal discharge or discomfort or itching.
In men and women who do oral sex without the protection of a condom(that is, they allow a penis into their mouth), these germs can infect the throat. Most of the time there are no symptoms when these germs are present in the back of the throat but sometimes the infected person may have symptoms of a sore throat. These diseases are not passed by kissing.
In men and women who do anal sex that is not protected by a condom (that is, they allow a penis to enter the anus), these germs can infect the rectum. Again there are usually no or very little symptoms with anal gonorrhea and chlamydia. When symptoms are present, there may be pus that comes out of the anus. There may be pain or the infected person may feel like he or she has to go to the bathroom often.
How is the diagnosis made?
A cue-tip or cotton swab is taken of the discharge and looked at under a microscope. A culture is also done. If no discharge is present, the swab is put into the opening of the penis or in the cervix of females and a culture is done. A culture is where the gonorrhea or chlamydia germ is grown on a chemical that is put in a incubator for a day or two. A culture of the throat or rectum may be taken if oral sex or anal sex has been done. Actually, in women we often take a culture of the rectum too since the germs sometimes spread to it even without anal intercourse.How are these diseases treated?
The two diseases have different treatments. Gonorrhea can be treated with an injection of an antibiotic or by a pill that just has to be taken once. Chlamydia is treated with an antibiotic that must be taken twice a day for a week or by four pills taken at once. A qualified health provider will be able to tell which medicine is best.Can these diseases cause serious problems?
If left untreated these two germs can cause serious problems in the infected individuals. In women, the germs can travel up through the uterus into the fallopian tubes and cause a serious disease called Pelvic Inflammatory Disease or PID . PID is very serious because the women may become sterile from this, that is, she may not be able to have any children in the future. The fallopian tubes are very fragile and an infection inside them can permanently scar them.Anatomy and Physiology of the Sexual Organs