

Anatomy of the Sex Organs
Q. What is anatomy and physiology and why study them?
Anatomy is what the parts of the body look like and physiology is how the various parts of the body work. In medical school, one of the very first things that we study is how the body looks and works. After we learn what these parts look like normally, we then learn how they look and work when they become diseased. It is important that we all learn as much as we can about our own bodies as we will have our bodies for all our lives and if we don't take care of them, no one else will. Women and girls should know where their cervix and ovaries are and men and boys should know what the testicles do and where the urethra is.
Anatomy of the genitals and reproductive tract
The genitals are the body parts involved with sex and the reproductive tract includes those body parts that are involved in sex that are inside our bodies.
Reproductive anatomy Diagrams
Female
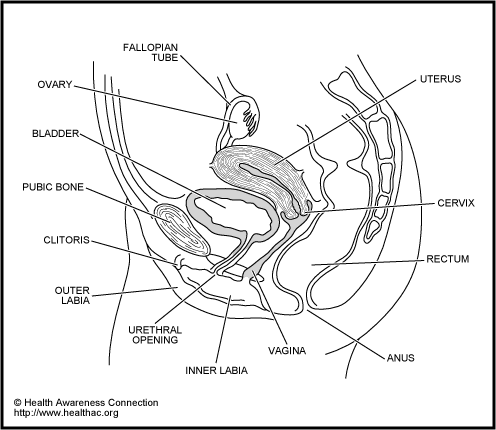
External (What is visible from the outside)
Even though these parts are on the outside, if a girl or woman wants to examine them she may want to use a mirror.
Labia - There are two pairs of labia or lips, the outer lips and the inner lips. They help to protect the opening to the urethra and the vagina. The outer labia may have some pubic hair on them.
Pubic Hair - Above the labia is the pubic hair which may be in a small area or may cover a large area on the lower abdomen. This hair develops during the teenage years and probably serves a protective function.
Clitoris - A small bump at the top of external genitals where the labia meet in the middle. It enlarges during sexual excitement and its function is in sexual functioning. It is covered by a hood or fold of skin to protect it.
Urethra opening - This lies below the clitoris and above the vaginal opening. It is where urine (pee) comes out of. The urethra is the tube inside from this opening to the bladder. The bladder is a collection area for urine inside our bodies.
Rectum - The rectum is the last part of the intestines and it is from where solid body wastes leave our body. The actual opening to the outside is called the anus or the anal opening. Although it is not a part of the sex organs, it is included here because infections can happen here from leakage from the vagina or from having anal intercourse.
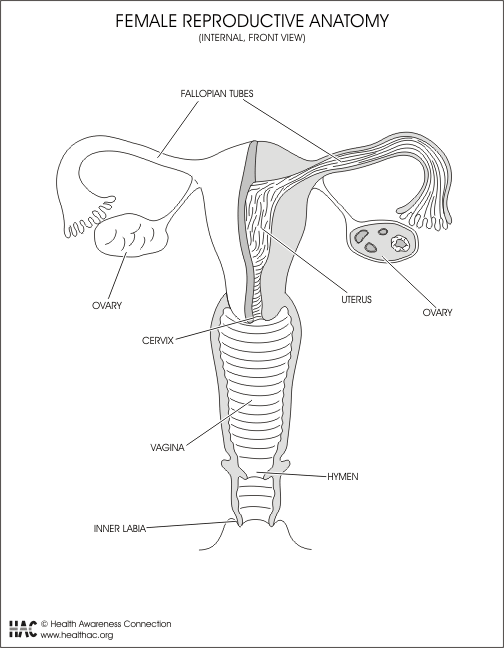
Inside (Internal)
Hymen - This is a ring of skin around the opening of the vagina that gets broken during sexual intercourse after which the women is no longer a virgin.
Vagina - This is a tube-like opening that is moist most of the time because it has some glands that produce vaginal fluids. The tube ends a few inches inside at the cervix. This is where the penis fits during intercourse and it is through this tube that a baby goes through when it is being born.
Cervix - This is the bottom end of the uterus. It has a small opening though which menstrual blood flows from the uterus. It is also the hole where semen can enter through and through which a baby comes out. This opening along with the vagina can expand greatly during childbirth to allow the baby to exit. When a doctor examines a woman, s/he will put a speculum (a tool to open the vagina) inside the vagina and look at the cervix for any abnormalities. The lining of the skin covering the cervix is different in young women who have not started to have their periods yet. This is important in the transmission of STDs since germs may be able to enter more easily in younger women.
Uterus - This a muscular organ that has an inner lining with a lot of blood vessels. The inner lining builds up every month and if the woman does not get pregnant, it is washed out and renewed every month. The blood that a woman loses every month during her period is this inner lining of the uterus. This blood rich inner lining provides the necessary environment for a developing embryo and fetus. The uterus is where a baby develops from an embryo into a fetus. It stretches greatly to hold the developing fetus and the muscles tighten up when the baby is due to be delivered. The uterus also contracts during menstruation ( the period) which causes cramps that are familiar to most women. One of the openings of the uterus is through the cervix which opens into the vagina. The other openings are at the other end and open into the fallopian tubes.
Fallopian Tubes - On each side of the uterus there is a narrow tube that reaches out towards the ovaries. It is through this tube that the egg travels from the ovary to the uterus. It is in this tube that fertilization takes place if the egg meets a sperm along the way.
Ovary - Women have two ovaries which are about the size of a flattened walnut(1X1 _"). The ovaries contain eggs which develop and enlarge during the menstrual cycle and then pop out near the opening of the fallopian tube. The tube catches the egg and transports it towards the uterus. About 300 to 400 eggs are produced during a women's life from the time she starts her period until she stops(menopause). The other function of the ovaries are to produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
Egg - The egg (also called an ovum or ova) is what gets together with a sperm to form a baby. If the egg travels down the tube without meeting a sperm, it doesn't get fertilized and it comes out with the menstrual flow of blood.
Breasts - The breasts are fatty tissues with milk producing glands inside. The breasts may swell and become tender before the period starts and they may also swell during sexual excitement. The nipple can become firm in the cold or to a touch. Sometimes there is a bit of hair around the nipple. It is common to have one breast slightly larger than the other.
Male
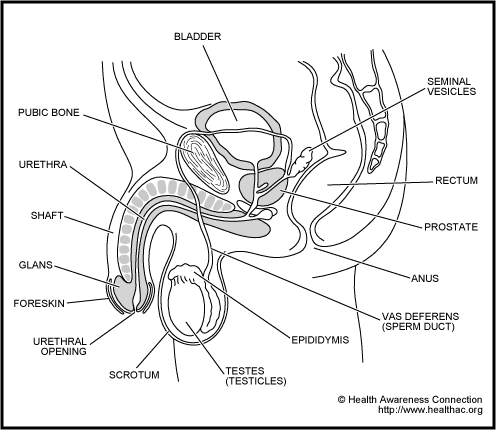
External (Outside organs)
Penis - this is the cylinder-like organ between males legs. It is normally hanging downward and when sexually excited, it becomes hard and enlarges.
Shaft - filled with a sponge-like tissue that can get filled with blood during sexual excitement and become erect and stiff. It is not a muscle.
Glans - the bulb-like area on the end of the shaft. This area is the most sensitive to sexual arousal. This is also called the head of the penis. In uncircumcised men it is covered by the foreskin.
Foreskin - the covering over the glans, it is cut off during circumcism. It can be pulled back and it also comes back by itself during erection.
Urethral opening - through this opening comes urine and semen. Germs can also enter into here.
Scrotum - The sac or bag that contains the testicles. The testicles are outside the body because they have to be at the right temperature to produce sperm. When it is warm outside, the scrotum relaxes and the testicles drop down away from the body so as to not get too hot. When it is cold, the scrotum tightens up and brings the testicles close to the body to keep them warm.
Pubic hair - appears after puberty and can be localized above the penis or can go up into the chest hair in some hairier men.
Rectum - The rectum is the last part of the intestines and it is from where solid body wastes leave our body. The actual opening to the outside is called the anus or the anal opening. Although it is not a part of the sex organs, it is included here because infections can happen here. On occasion warts can spread from the front of a man to the back. Also many other STDs can be spread to the anal area by having anal sex.
Internal
Urethra - the tube inside the penis shaft. Urine and semen go through it. Just the opening is visible at the end of the penis. It is the place where such STDs such as gonorrhea and chlamydia can live.
Prostate - This gland produces some of the semen that comes out when a man has an orgasm. The prostate can be infected with some of the germs that cause STDs such as gonorrhea or chlamydia. The germs are harder to get rid of when they get into the prostate and antibiotic medicine usually has to be given for a longer time. The prostate gland is examined by health providers by doing a rectal exam. In this exam, the doctor or health provider puts a gloved finger into the anus. The prostate can be felt under his or her finger.
Seminal Vesicles - these glands produce some of the semen that comes out when a man has an orgasm.
Vas deferans - this tube connects the testicles with the urethra and carries sperm.
Testes (also called the testicles) - These are the 'balls' inside the scrotum. Their purpose is to make sperm and to produce the male hormone, testosterone.
Epididymis - This is the area on top of the testicle that collects sperm and connects with the vas deferans. If some STDs such as gonorrhea or chlamydia are left untreated, the germs can get into the epididymis and cause them to swell up and become tender.
Physiology (How it works)
The menstrual cycle
The changes that go on in a women's body are very complicated but the main purpose is to prepare a women's body to get pregnant.
The first day of the cycle is the first day of bleeding. Since pregnancy did not occur, the hormones(estrogen and progesterone) stop being produced and the lining of the uterus falls off and comes out of the vagina as blood and clots.
During the first few days of the cycle, the ovary (on one side or the other) is producing follicles which contain an egg and are secreting estrogen. One of these eggs matures. The increase of estrogen that is being secreted by the maturing eggs signals the brain to release other hormones and it signals the uterus to develop. The hormones from the brain (actually the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus) signals the ovary to release its egg (called ovulation). After the egg is released, the left over follicle keeps on producing estrogen and also produces progesterone. There is a complex interaction between the hormones from the brain and those from the female sex organs.(see below)
After ovulation, the egg travels down the tube on its way toward the uterus. If it meets a sperm along the way, they may join together (fertilization) and start to form an embryo which lands in the blood rich lining of the uterus and there it grows into a fetus.
Hormones
Estrogen - A chemical made by the ovaries that has many effects on women's bodies including:
- development of the female reproductive organs (Vagina, uterus, breasts) during puberty.
- signaling the brain and the reproductive organs during the menstrual cycle to have effects.
- giving women their shape by regulating fatty layers.
- Stopping the growth of bones (most girls do not grow much after puberty).
- Many chemical functions in the body.
Progesterone - made by the ovary in the second half of the menstrual cycle and during pregnancy. It, like estrogen, has many functions including:
- preparing the uterus to accept a fertilized egg.
- helping to regulate the menstrual cycle.
- helping to maintain a healthy uterus during pregnancy.
Vaginal secretions - the inside of the vagina is made a type of skin called mucus membrane. This type of skin, like the inside of our mouths, is normally moist or wet. When a woman is sexually excited, the lining of the vagina makes more wetness.
Puberty
This is a time in a young person's life when there sexual organs become mature. The hormones that affect sexual urges get active during this time and affect the different parts of the body.
In girls, their bodies are changing to develop the curves of the hips and the breasts. Body hair in the armpits and in the genital area develops. The girls sex organs mature and the menstrual period begins. Puberty usually begins between the age of nine to fifteen.
In boys the period of puberty usually begins later than in girls. Body hair starts to develop, their voice becomes lower and the sex organs get larger and they are able to make sperm.
In both boys and girls the hormonal changes in the body make them have strong sexual feelings. Boys will get an erection easily by just thinking about sex. Both boys and girls will get a warm, tingling feeling in their bodies especially in their private parts. These feelings are very powerful and it is important to learn to handle them. All grownups get these feelings and they have learned to control them.
How babies are made and prevented
As mentioned in the discussion of the menstrual cycle, an egg gets released by an ovary each month in women and if it meets a sperm in the right place in the fallopian tube it becomes fertilized and starts to grow into a baby. Babies can be prevented by not allowing the egg and sperm to get together.
Birth control methods
Abstinence (not having sex) is the most effective way to avoid having babies or getting an STD. If you don't have sex, you can't get pregnant or get an STD. Even though it sometimes doesn't seem like it, many teens are not having sex. Many teens wait until they are older before becoming sexually active.
The birth control pill is a very common and very effective form of birth control. The pill (also called oral contraceptives) stops an egg from being released from the ovary. The advantage of the pill is that it is very effective and the woman does not have to do anything else except take a pill once a day. Its disadvantage is that it does not protect the woman against STDs or HIV disease so a condom should be used along with taking the pill to avoid these diseases.
Condoms ("rubbers") have been used to prevent women from getting pregnant for a long time. They are very effective if used properly and they have the added benefit of helping to prevent STDs and HIV disease. If you choose to have sex, condoms may be the most important thing you can do to protect yourself from an unwanted pregnancy and sexually transmitted diseases and HIV infection. When condoms were first invented over a hundred years ago, they were made of sheep's intestines and it is still possible to find lambskin condoms which are the same. These type of condoms will not fully protect you against STDs and should not be used. Instead, you should always use latex condoms which are made of a type of rubber.
The diaphragm is an effective means of birth control. It is a round rubber shield-like barrier that is put inside the vaginal before having sex. It is filled with a jelly or cream that contains a chemical (called nonoxynol-9) that kills sperm. Although it has some protection against STD's, It is not very effective for this and condoms should be used along with the diaphragm for protection.
A newer form of birth control is a hormone injection or implant that can prevent pregnancy. The injection is given every three months or it is placed under the skin where it is slowly released into the body.
The IUD or intrauterine device is a piece of special wire that is placed into the uterus by a health provider where it can stay for years. It disturbs the environment inside the uterus making it not possible to have a fetus growing in it. There is a small string that dangles out of the cervix to allow for its removal. Its disadvantage is that it offers no protection against STDs and AIDS. It is no longer as commonly used as it used to be partially because having an IUD may make a woman more likely to get STDs because of the string that sticks out into the vagina.
Some couples use a technique called withdrawal or the rhythm method to prevent getting pregnant. In this technique, the man withdraws or pulls out his penis from the vagina just before he has an orgasm (comes). Since no semen enters the vagina, the woman cannot get pregnant. This method has several problems. First of all it offers no protection against STDs. It is also very difficult to time the withdrawal properly when the couple is in the heat of passion and some semen may enter the vagina. Also, before a man comes, a small amount of fluid(called pre-ejaculatory fluid) is released by the penis and this enters the woman. This fluid, although it is only a small amount, may contain some semen and the woman may get pregnant.
Although it is not a real birth control method, abortion is a way to end a pregnancy. In an abortion, the developing fetus is removed from the uterus and it cannot survive outside. If it is early in the pregnancy, the uterus is scraped with a tool that is pushed through the cervix. If it is late in the pregnancy, some water is injected into the uterus and this stops the pregnancy and the fetus is pushed out through the vagina as in a normal delivery of a baby. There is a lot of controversy about abortions since many people believe it is the same as killing a human being. Of course it is better to avoid getting pregnant than to have to be in the position of thinking about abortion.
Sterilization is a means of permanently changing the normal anatomy so it is impossible to have a child. In women, the fallopian tubes are cut and the ends are sown up. This prevents an egg (or sperm) from traveling down the tube. In men, the vas deferens is cut and the ends sown up to prevent sperm from traveling from the testicles to the urethra. This is called a vasectomy. Although I said these were permanent changes, it is possible to reconnect these tubes in both men and women but it is a difficult operation and it doesn't always work.
Male Physiology
Testicular function - When a boy starts to get physically mature, the testicles start to produce more testosterone which is the male sex hormone. The testicles also become able to produce sperm .
Testosterone - the male sex hormone gives boys and men the lower voice, the hair on the face and body, and the bulkier muscles. Since girls have much less of this hormone, they have higher voices, less body hair and less bulging muscles.
Sperm production - Takes place in the testicles and is controlled by the hormone testosterone.
Semen - this is the fluid that squirts out of the penis when a man has an orgasm. It is made of three fluids. Most of it (90-95%) comes from the prostate gland and the seminal vesicles and only a small part of it is actual sperm which comes from the testicles.
Libido - this is the sex drive or urge that men (& women) have. A persons libido increases during the teen years since the hormones that control this increases during these years.
Erection (include size of penis) - The penis increases in size during sexual excitement because it gets filled with blood. There usually seems to be a lot of concern with the size of the penis in boys (and men). There is a big difference in the size of the penis when it is erect or not erect. In adult men the erect size varies from five to seven inches but it may be smaller or bigger in some cases. Teenage boys can get an erection easily since they have a new increase in the sex hormone testosterone.
Orgasm - During sex with another person or alone (called masturbation), a climax is reached where semen squirts out of the urethral opening. An intense feeling occurs which lasts for a very short time.